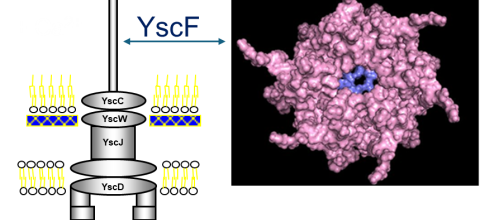
Yersinia pestis, the bacterium that causes the bubonic plague, uses a type III secretion system (T3SS) to inject toxins into host cells. The structure of the Y. pestis T3SS needle has not been modeled using AI or cryo-EM. T3SS in homologous bacteria have been solved using cryo-EM. Previously, we created possible hexamers of the Y. pestis T3SS needle protein, YscF, using CollabFold and AlphaFold2 Colab on Google Colab in an effort to understand more about the needle structure and calcium regulation of secretion. Hexamers and mutated hexamers were designed using data from a wet lab experiment by Torruellas et. al (2005). T3SS structures in homologous organisms show a 22 or 23mer structure where the rings of hexamers interlocked in layers. When folding was attempted with more than six monomers, we observed larger single rings of monomers. This revealed the inaccuracies of these online systems. To create a more accurate complete needle structure, a different computer software capable of creating a helical polymerized needle is required. The number of atoms in the predicted final needle is very high and more than our computational infrastructure can handle. For that reason, we need the computational resources of a supercomputer. We have hypothesized two ways to direct the folding that have the potential to result in a more accurate needle structure. The first option involves fusing the current hexamer structure into one protein chain, so that the software recognizes the hexamer as one protein. This will make it easier to connect multiple hexamers together. Alternatively, or additionally the cryo-EM structures of the T3SS of Shigella flexneri and Salmonella enterica Typhimurium can be used as models to guide the construction of the Y. pestis T3SS needle. The full AlphaFold library or a program like RoseTTAFold could help us predict protein-protein interactions more accurately for large structures. Based on our needs we have identified the TAMU ACES, Rockfish and Stampede-2 as promising resources for this project. The generated model of the Y. pestis T3SS YscF needle will provide insight into a possible structure of the needle.